Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Morii, Shiori; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 37(12), p.1843 - 1846, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we developed a simple and one-step Pd separation technique based on photoreduction with Xe lamp irradiation for the determination of  Pd in highly radioactive samples. A simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) solution, which consists of 14 major elements (Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) in a 3 mol L
Pd in highly radioactive samples. A simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) solution, which consists of 14 major elements (Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) in a 3 mol L HNO
HNO solution, was used to evaluate the separation performance. The Pd precipitate were formed by Xe lamp irradiation and recovered by centrifugation. The results showed that the recovery of Pd from a simulated HLLW solution depend on the irradiation time and concentration of ethanol. By optimizing the conditions at photo irradiation, the Pd recovery from the simulated HLLW solution reached up to 50 %, while 99.5 % of the other 13 elements were separated. The Pd precipitate could be separated from the elements that are the main source of radioactivity (Sr, Cs, and Ba) and the source of spectral interference for the determination of
solution, was used to evaluate the separation performance. The Pd precipitate were formed by Xe lamp irradiation and recovered by centrifugation. The results showed that the recovery of Pd from a simulated HLLW solution depend on the irradiation time and concentration of ethanol. By optimizing the conditions at photo irradiation, the Pd recovery from the simulated HLLW solution reached up to 50 %, while 99.5 % of the other 13 elements were separated. The Pd precipitate could be separated from the elements that are the main source of radioactivity (Sr, Cs, and Ba) and the source of spectral interference for the determination of  Pd (Zr, and Ru). These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the proposed method, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Pd (Zr, and Ru). These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the proposed method, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
 , an iodine source for the immobilisation of radioiodine
, an iodine source for the immobilisation of radioiodineJohnstone, E. V.*; Bailey, D. J.*; Lawson, S.*; Stennett, M. C.*; Corkhill, C. L.*; Kim, M.*; Heo, J.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Hyatt, N. C.*
RSC Advances (Internet), 10(42), p.25116 - 25124, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.55(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yomogida, Takumi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123(1), p.817 - 824, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:53.94(Chemistry, Physical)Reaction kinetics of laser-induced particle formation in an aqueous solution of PdCl
 was investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS). The Pd particle was generated by irradiation of nanosecond pulsed 266-nm laser. The TEM observation showed dependence of the particle size on the laser fluence and promotion of the particle growth by irradiation of high-fluence laser. The DXAFS data give us the Pd
was investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS). The Pd particle was generated by irradiation of nanosecond pulsed 266-nm laser. The TEM observation showed dependence of the particle size on the laser fluence and promotion of the particle growth by irradiation of high-fluence laser. The DXAFS data give us the Pd concentration. Temporal changes of the Pd
concentration. Temporal changes of the Pd concentration analyzed based on Finke-Watzky two step mechanism. The analysis elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the reduction of the PdCl
concentration analyzed based on Finke-Watzky two step mechanism. The analysis elucidates that the laser photon contributes to the reduction of the PdCl
 ion by the one-photon process and to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles by the multi-photon process.
ion by the one-photon process and to the autocatalytic growth of the Pd particles by the multi-photon process.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Asai, Shiho; Oba, Hironori*
Bunseki, 2018(4), p.138 - 143, 2018/04
Platinum group metal (PGM) has attracted much attention in light of increasing demands in the industrial sector. A wide variety of techniques specialized for PGM separation, such as, solvent extraction, solid phase extraction, and molten salt electrolysis have been developed so far. Among such techniques, a newly developed separation technique based on laser-induced particulate formation can be a promising alternative to conventional ones. It enables non-contact and highly-selective separation with a simple operation. In this review, the research history and the basic mechanism of laser-induced particulate formation were outlined. Several applications were also mentioned, focusing on our latest research progress which achieved a world first quantitation of radioactive palladium in a spent nuclear fuel sample.
Narita, Hirokazu*; Maeda, Motoki*; Tokoro, Chiharu*; Suzuki, Tomoya*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Analytical Sciences, 33(11), p.1305 - 1309, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:40.7(Chemistry, Analytical)Saeki, Morihisa*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Oba, Hironori*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Yomogida, Takumi
Denki Gakkai Kenkyukai Shiryo, Denshi Zairyo Kenkyukai (EFM-17-010 021), p.15 - 18, 2017/09
021), p.15 - 18, 2017/09
Irradiation of nanosecond pulsed UV laser into a solution of palladium ion leads to formation of palladium particles with sub-micron size particles by time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Morita, Yasuji; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Research 2017-006, 27 Pages, 2017/06
Separation of Pd by extraction with 5,8-diethyl-7-hydroxy-6-dodecanone oxime (DEHDO) was examined by batch and continuous tests for the purpose of developing Pd separation process. Batch extraction tests using n-dodecane solution of DEHDO revealed that Pd, Zr and Mo were extracted from simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) and other elements were not, and also showed that the extraction rate was a little slow and a white precipitate appeared in the aqueous phase but its formation could be avoided by raising temperature. The extracted Pd was found to be back-extracted with sodium nitrite. In the continuous extraction tests with simulated HLLW without Zr and Mo, about 98% of Pd were extracted with DEHDO-n-dodecane and 95% of the extracted Pd were back-extracted with sodium nitrite and nitric acid. Continuous extraction test with simulated HLLW with Zr and Mo showed the possibility of the simultaneous separation of Pd and Mo by DEHDO extraction.
 X-ray absorption spectroscopy study on water formation reaction of palladium metal nanoparticle catalysts
X-ray absorption spectroscopy study on water formation reaction of palladium metal nanoparticle catalystsMatsumura, Daiju; Taniguchi, Masashi*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; Nishihata, Yasuo
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(11), p.7749 - 7754, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:14.05(Chemistry, Physical) O
O studied by time-resolved XAFS using dispersive optics
studied by time-resolved XAFS using dispersive opticsMatsumura, Daiju; Okajima, Yuka*; Nishihata, Yasuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 712(1), p.012042_1 - 012042_4, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Physics, Applied)Abe, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Sato, Fumiatsu*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 404-406, p.288 - 292, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.67(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of ion irradiation on the rate of electrochemical hydriding rate of palladium (Pd) was investigated. In this study, ion irradiation onto the Pd surface was made with H , He
, He , Ar
, Ar and N
and N in the acceleration energy range from 30 to 350 keV, and in the ion dose up to 1
in the acceleration energy range from 30 to 350 keV, and in the ion dose up to 1  10
10 cm
cm . As the ion dose was increased, the initial rate of hydriding of Pd was increased. The ion irradiatiion treatment of the surface of a metal induces high concentrations of vacancy. The increased hydriding rate may be caused by the induction of high concentration of vacancy whichi traps hydrogen atoms, and this seems to accelerate the rates of hydride nucleation and growth in the surface. The ion irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of Pd in the electrochemical hydriding process.
. As the ion dose was increased, the initial rate of hydriding of Pd was increased. The ion irradiatiion treatment of the surface of a metal induces high concentrations of vacancy. The increased hydriding rate may be caused by the induction of high concentration of vacancy whichi traps hydrogen atoms, and this seems to accelerate the rates of hydride nucleation and growth in the surface. The ion irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of Pd in the electrochemical hydriding process.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Uzawa, Masayuki*; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.63 - 66, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Meguro, Yoshihiro; Ogiyanagi, Jin*; Tomioka, Osamu; Imura, Hisanori*; Ohashi, Kozaburo*; Yoshida, Zenko; Nakashima, Mikio
Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Supercritical Fluid Technology for Energy and Environment Applications (Super Green 2003), p.175 - 179, 2004/00
One of the most attractive properties of SFE is that changing solvent properties by tuning pressure can control distribution behavior of a metal ion. Distribution ratio (D) of uranium(VI) and plutonium(IV) with tributyl phosphate (TBP) from a nitric acid solution and palladium(II) with 2-methyl-8-qunolinol (HMQ) from a hydrochloric solution were determined in SFE at various pressures. In the extraction system using TBP, a linear relationship between the logarithmic distribution ratio (log D) and the solubility parameter of CO was observed. The solubility parameter is difined based on the regular solution theory and is one of the parameters depending on the pressure. On the other hand, a linear relationship with a positive slope between log D and the solubility parameter was observed in the extraction system using HMQ. Most of the extractant was dissolved in the aqueous phase as H
was observed. The solubility parameter is difined based on the regular solution theory and is one of the parameters depending on the pressure. On the other hand, a linear relationship with a positive slope between log D and the solubility parameter was observed in the extraction system using HMQ. Most of the extractant was dissolved in the aqueous phase as H MQ
MQ under the extraction condition examined.
under the extraction condition examined.
Abe, Hiroshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uedono, Akira*; Chen, Z. Q.*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.224 - 227, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:78.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)Palladium(Pd) is used for the purification of H gas and as a catalyst for the dissociation of H
gas and as a catalyst for the dissociation of H molecules. Therefore, much work has been made until now. Since low energy ion irradiation, i.e., ion implantation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydrogen absorption properties of Pd is expected to be improved by ion irradiation. In this work, we aimed at investigating the effect of ion irradiation on the hydrogen absorption rate of Pd. Ion irradiation was made with H
molecules. Therefore, much work has been made until now. Since low energy ion irradiation, i.e., ion implantation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydrogen absorption properties of Pd is expected to be improved by ion irradiation. In this work, we aimed at investigating the effect of ion irradiation on the hydrogen absorption rate of Pd. Ion irradiation was made with H , He
, He and Ar
and Ar in an acceleration energy rage from 30 to 350keV up to a dose of 1 x 10
in an acceleration energy rage from 30 to 350keV up to a dose of 1 x 10 /cm
/cm . As a result, ion irradiated Pd sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the unirradiated one. The initial hydrogen results suggest that defects introduced in Pd by ion irradiation facilitate tha rate of nucleation and growth of hydride.
. As a result, ion irradiated Pd sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the unirradiated one. The initial hydrogen results suggest that defects introduced in Pd by ion irradiation facilitate tha rate of nucleation and growth of hydride.
Nishihata, Yasuo; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
SPring-8 Riyosha Joho, 7(6), p.359 - 363, 2002/11
Catalytic converters are widely applied to control automotive emissions, such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons. In actual catalysts, however, the catalytic activity deteriorates due to the particle growth of precious metals during vehicle use. An ageless catalyst is a kind of philosopher's stone in automotive engineering. Referring to the wisdom of ancient Indian philosophy and medical science, Ayur Veda, we have developed a new self-regenerating perovskite-based catalyst. The perovskite catalyst, LaFe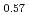 Co
Co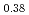 Pd
Pd O
O , regenerates itself without any auxiliary treatment, in direct reaction to the natural fluctuation between reductive and oxidative atmospheres in the exhaust gas from state-of-the-art gasoline engines. As palladium reversibly moves back and forth between inside and outside of the perovskite crystal, the particle growth of palladium can be suppressed. Such a self-regeneration provides new insight into the development of future automotive catalyst, as an intelligent catalyst.
, regenerates itself without any auxiliary treatment, in direct reaction to the natural fluctuation between reductive and oxidative atmospheres in the exhaust gas from state-of-the-art gasoline engines. As palladium reversibly moves back and forth between inside and outside of the perovskite crystal, the particle growth of palladium can be suppressed. Such a self-regeneration provides new insight into the development of future automotive catalyst, as an intelligent catalyst.
Tominaga, Shinya*; Busnyuk, A.*; Matsushima, T.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Ono, Futaba*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Fusion Science and Technology, 41(3), p.919 - 923, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
Tamada, Masao
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (93), p.17 - 21, 2002/03
Radiation induced graft polymerization is useful technique for introducing aiming function into conventional polymers. Especially, preirradiation method can easily control the graft yield by irradiation dose and polymerization time. In this method, storing the irradiated polymer at low temperature is capable of grafting at discrete facility, which is merit for industrialization. Removal of toxic metals with grafted polymer needs the functions of ion exchange and chelating reaction. Graft polymerization is superior method to introduce such functions into the polymer. The fibrous adsorbent for lead ion, prepared by grafting, shows the high performance to the particle adsorbent.
Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Tamura, Kazuhisa*; Kondo, Toshihiro*; Uosaki, Kohei*
Shinku, 44(3), P. 375, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Masamitsu; Hayashi, Yukio; Mizuki, Junichiro; Tamura, Kazuhisa*; Kondo, Toshihiro*; Naohara, Hideo*; Uosaki, Kohei*
Surface Science, 461(1-3), p.213 - 218, 2000/08
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:91.97(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Fujii, Toshiyuki*; *
JNC TJ9400 2000-003, 36 Pages, 2000/02
For establishing a recycling system based on low-decontamination, the distribution behaviors of radionuclides in the process are essential information for the design of the system. Molybdenum and palladium are less radioactive fission products, but attention should be paid to them because they are likely to extremely affect the performance of the recycled fuels. In this context, in this study, the extraction behaviors of molybdenum and palladium under conditions of PUREX and TRUEX extraction process were experimentally studied, and their chemical mechanisms were discussed. In cojunction with the extraction experiments, absorption spectrometry was applied to identify the related species and the extraction mechanism. As a result, knowledge for the distribution characteristics of molybdenum and palladium in PUREX and TRUEX process was reinforced.
; ; Sato, Haruo; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-088, 58 Pages, 1999/06
Sorption and diffusion behavior of palladium, which has been identified as one of the hazardous radionuclides in performance assessment of HLW disposal, in bentonite, granodiorite and tuff was studied in order to make reliable data set for the performance assessment. Sorption experiments of Pd on bentonite, granodiorite and tuff were conducted as functions of pH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio by batch method under aerobic conditions at room temperature. The distribution coefficients (K ) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10
) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /kg and were in the order of bentonite
/kg and were in the order of bentonite  granodiorite
granodiorite  tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K
tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K
values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K was not found in a range of 10
was not found in a range of 10 to 10
to 10 , but K
, but K values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K
values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m
was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m /kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH)
/kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH) (aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K
(aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K
values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH
values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO
type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D
sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...
values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...